[Trade Journal]
Publication: The Journal of Electricity, Power and Gas
San Francisco, CA, United States
p. 329, col. 1-2
A NEW STRAIN INSULATOR SWITCH.
The Pacific Electric Manufacturing Company of San Francisco has recently designed a switch on which the line wires can be directly dead-ended. It may be equipped with one of several standard strain insulators, which can lie quickly and easily removed and replaced by other standard strain insulators, without cementing any special parts, and solely by loosening three bolts.
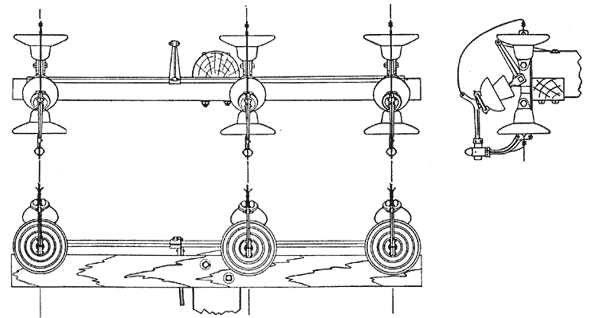 |
| Diagram of Strain Insulator Switch. |
As the blade moves in a line parallel to the line wires and no conducting members extend to either side, the switches are spaced no further apart than the standard centers of the line wires. The switch is retained in the closed or open position by gravity. The strain insulators are immovable, and no strain, either mechanical or electrical, is added to their customary., functions as strain insulators. The arc is drawn far above the porcelain.
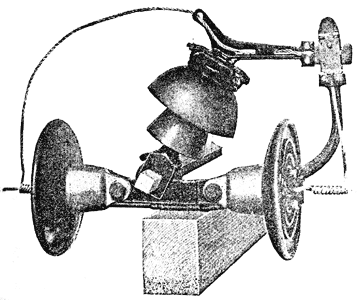 |
| End View of One of the Units of the Strain Insulator Switch Showing Adaptation of Standard Type of Insulator. |
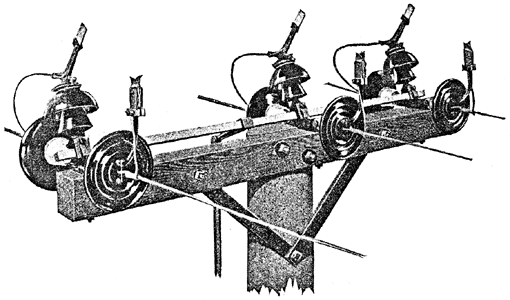 |
| Strain Insulator Switch in Open Position on Pole. |
The switch is group controlled by a square rocker shaft, having bearings bushed with brass, and the three units can be set at any position on this shaft, making this switch one that is particularly easy to install.
All wrought iron and malleable parts are galvanized or sherardized. This switch can be furnished fully equipped with insulators or equipped with the pin insulators only, the strain insulators to be furnished by the purchaser. It can be installed on a single crossarm of the purchaser's standard length.