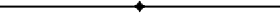[Trade Journal]
Publication: Western Electrician
Chicago, IL, United States
vol. 36, no. 15, p. 292, col. 1-2
High-potential Laboratory for Insulator
Testing.
In the manufacture of .insulators for high-tension work an important part of the factory equipment is the high-potential testing apparatus which is necessary to the manufacturer that he may know that his product is up to the rigorous standards necessary in this class of construction. The Locke Insulator Manufacturing Company of Victor, N. Y., has a well-equipped laboratory for this purpose, and Fig. 1 of the accompanying illustrations shows the motor-generator set in this laboratory.
The laboratory is full fireproof construction, measuring 20 by 48 feet. The foundations and floor are of heavy concrete, designed to carry the heavy machinery without communicating vibrations to any delicate apparatus.
| |||
| Fig. 1. High-Potential Laboratory for Insulator Testing. High-Tension Insulators and Methods of Testing. |
The electrical equipment includes a transformer with a guaranteed capacity of 200 kilowatts at 300,000 volts. It is of the core type, with approximately 10 by 10 inches cross-section of iron and has a primary wound for 1,100 volts, made up of four wires in parallel, allowing of some flexibility in connection. The secondary consists of approximately 42 miles of No. 26 wire, which, under oil, will carry 100 per cent. overload for considerable periods of time and at an overload potential of 400,000 volts this transformer is one of the most powerful electrical testing equipment in present use. The secondary winding is divided into two parts which can be connected in parallel or series, giving full loads at low potentials.
| |||
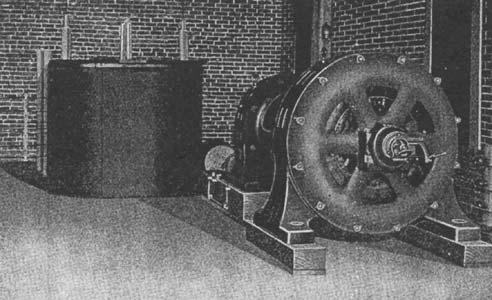
| Fig. 2. Arcing Over An Insulator During A Rain Test at 40,000 Volts. High-Tension Insulators and Methods of Testing. |
Current for the primary of the transformer is provided by a motor-generator set, power for which is obtained from a local transmission line. The set consists of a 440-volt, three-phase, 25-cycle, 200-kilowatt induction motor direct connected by flexible coupling to a 60-cycle, 1,100-volt, single-phase generator of similar capacity. For purposes of experimentation or for special commercial test requirements, higher or lower frequency is obtained by belt connection, using various sizes of pulleys.
The controlling switches for the generating set are located on a slate board placed so that the operator can overlook any test being carried on in the commercial testing room nearby. Ordinary controlling switches and rheostats, together with instruments, are located on this board.
 |
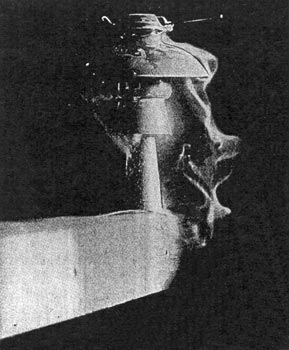
| Fig. 3. Type of High-Tension Wall Insulator. High-Tension Insulators and Methods of Testing. |
To facilitate measurements of secondary voltages a spark gap, adjustable by hand, is provided with a scale calibrated to 480,000 volts,, enabling a test of any material to be made. For more accurate measurement of the high voltages a secondary voltmeter has been installed. This instrument submerged in oil transfers its readings by means of a mirror to a calibrated scale, which is read by means of a telescope. The very small secondary currents are measured by means of an inclined-coil instrument inserted at the point of earth potential of the secondary winding.
Extending some distance from the laboratory is an experimental pole line of standard poles and cross-arms adapted to receive any style of pins or insulators, whose distances apart may be varied.
A simple form of dynamometer provides facilities for the testing of tensile and crushing strength of insulators and insulating materials. For the study of very refractory substances an electric furnace capable of absorbing 200 kilowatts is provided.
Fig. 2 illustrates an actual test being made on an insulator mounted on a metal pin and cross-arm. The arc, which is well shown in the picture, took place during a rain test at 40,000 volts. The precipitation was three-fourths inch a minute.
The company manufactures many creditable types of insulators, among which is a wall insulator (Fig. 3) for high-tension work. These wall insulators may be used in passing high-potential wires out of and into the power, house or sub-station and can also be used as insulation in the wall between high-potential transformer compartments. When used in this way they serve as full fire protection between the compartments, presenting a great abundance of mechanical strength as well as efficient insulation.